当多个线程使用共享对象的时候,依次等待,这种我们通常叫着线程同步;下面介绍几种线程同步的方法:
原子操作
所谓原子操作是指不会被线程调度机制打断的操作;用于执行轻量级、仅执行一次的操作,比如修改计数器,某些条件下的增加值或设置位等。这种操作一旦开始,就一直运行到结束,中间不会有任何 context switch(切换到另一个线程)。
internal class Program { private static void Main(string[] args) { Console.WriteLine("Incorrect counter"); var c = new Counter(); var t1 = new Thread(() => TestCounter(c)); var t2 = new Thread(() => TestCounter(c)); var t3 = new Thread(() => TestCounter(c)); t1.Start(); t2.Start(); t3.Start(); t1.Join(); t2.Join(); t3.Join(); Console.WriteLine("Total count: {0}", c.Count); Console.WriteLine("--------------------------"); Console.WriteLine("Correct counter"); var c1 = new CounterNoLock(); t1 = new Thread(() => TestCounter(c1)); t2 = new Thread(() => TestCounter(c1)); t3 = new Thread(() => TestCounter(c1)); t1.Start(); t2.Start(); t3.Start(); t1.Join(); t2.Join(); t3.Join(); Console.WriteLine("Total count: {0}", c1.Count); Console.ReadKey(); } static void TestCounter(CounterBase c) { for (int i = 0; i < 100000; i++) { c.Increment(); c.Decrement(); } } class Counter : CounterBase { private int _count; public int Count { get { return _count; } } public override void Increment() { _count++; } public override void Decrement() { _count--; } } class CounterNoLock : CounterBase { private int _count; public int Count { get { return _count; } } public override void Increment() { Interlocked.Increment(ref _count); } public override void Decrement() { Interlocked.Decrement(ref _count); } } abstract class CounterBase { public abstract void Increment(); public abstract void Decrement(); } } 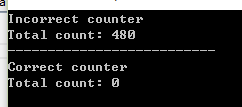
Mutex
同步基元,可以用于进程同步;当然也可以用于线程同步;
线程使用Mutex.WaitOne()方法等待C# Mutex对象被释放,如果它等待的C# Mutex对象被释放了,它就自动拥有这个对象,直到它调用Mutex.ReleaseMutex()方法释放这个对象,而在此期间,其他想要获取这个C#Mutex对象的线程都只有等待。
1.线程同步
static void Main(string[] args) { for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) { Thread t = new Thread(() => method()); t.Start(); } Console.ReadKey(); } static int count = 0; static Mutex mutex = new Mutex(); static void method() { Thread.Sleep(1000); mutex.WaitOne(); Console.WriteLine("当前数字:{0}", ++count); mutex.ReleaseMutex(); } 
2.进程同步
static void Main(string[] args) { const string MutexName = "CSharpThreadingCookbook"; using (var m = new Mutex(false, MutexName)) { if (!m.WaitOne(TimeSpan.FromSeconds(5), false)) { Console.WriteLine("Second instance is running!"); } else { Console.WriteLine("Running!"); Console.ReadLine(); m.ReleaseMutex(); } } Console.ReadKey(); } 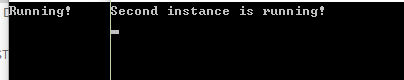
运行两个exe程序,得到执行结果
SemaphoreSlim
类表示一个轻量、快速的信号量,可在等待时间预计很短的情况下用于在单个进程内等待。 尽可能多地依赖公共语言运行时 (CLR) 提供的同步基元。 但是,它还提供延迟初始化、基于内核的等待句柄,作为在多个信号量上进行等待的必要支持。 也支持使用取消标记,但不支持命名信号量或使用用于同步的等待句柄。
对可同时访问资源或资源池的线程数加以限制的 的轻量替代。
Wait() 阻止当前线程,直至它可进入SemaphoreSlim 为止。
Release() 退出 SemaphoreSlim 一次。
static void Main(string[] args) { for (int i = 0; i <= 6; i++) { string threadName = "线程" + i; var t = new Thread(() => AccessDatabase(threadName)); t.Start(); } Console.ReadKey(); } // 同时授予4个信号量的初始请求数。 static SemaphoreSlim _semaphore = new SemaphoreSlim(4); static void AccessDatabase(string name) { Console.WriteLine("{0}等待进入", name); _semaphore.Wait(); Console.WriteLine("{0}进入", name); Thread.Sleep(2000); Console.WriteLine("{0}完成", name); _semaphore.Release(); } 
AutoResetEvent
允许线程通过发信号互相通信。通常,此通信涉及线程需要独占访问的资源。
线程通过调用 AutoResetEvent 上的 WaitOne 来等待信号。如果 AutoResetEvent 处于非终止状态,则该线程阻塞,并等待当前控制资源的线程通过调用 Set 发出资源可用的信号。
调用 Set 向 AutoResetEvent 发信号以释放等待线程。AutoResetEvent 将保持终止状态,直到一个正在等待的线程被释放,然后自动返回非终止状态。如果没有任何线程在等待,则状态将无限期地保持为终止状态。
可以通过将一个布尔值传递给构造函数来控制 AutoResetEvent 的初始状态,如果初始状态为终止状态,则为 true;否则为 false。
通俗的来讲只有等myResetEven.Set()成功运行后,myResetEven.WaitOne()才能够获得运行机会;Set是发信号,WaitOne是等待信号,只有发了信号,等待的才会执行。如果不发的话,WaitOne后面的程序就永远不会执行。
const int numIterations = 10; static int number; static AutoResetEvent myResetEvent = new AutoResetEvent(false); static AutoResetEvent ChangeEvent = new AutoResetEvent(false); static void Main(string[] args) { Thread payMoneyThread = new Thread(new ThreadStart(PayMoneyProc)); payMoneyThread.Name = "付钱线程"; Thread getBookThread = new Thread(new ThreadStart(GetBookProc)); getBookThread.Name = "取书线程"; payMoneyThread.Start(); getBookThread.Start(); for (int i = 1; i <= numIterations; i++) { Console.WriteLine("买书线程:数量{0}", i); number = i; myResetEvent.Set(); Thread.Sleep(1000); ChangeEvent.Set(); Thread.Sleep(1000); } Console.ReadKey(); } static void PayMoneyProc() { while (true) { myResetEvent.WaitOne(); Console.WriteLine("{0}:数量{1}", Thread.CurrentThread.Name, number); } } static void GetBookProc() { while (true) { ChangeEvent.WaitOne(); Console.WriteLine("{0}:数量{1}", Thread.CurrentThread.Name, number); Console.WriteLine("------------------------------------------"); } } 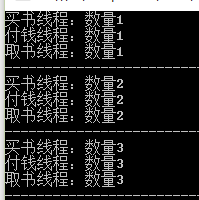
ManuualResetEventSlim
ManualResetEvent 类的简化版;通知一个或多个正在等待的线程已发生事件。static void Main(string[] args) { var t1 = new Thread(() => Method("线程1", 5)); var t2 = new Thread(() => Method("线程2", 6)); var t3 = new Thread(() => Method("线程3", 12)); t1.Start(); t2.Start(); t3.Start(); Thread.Sleep(TimeSpan.FromSeconds(6)); Console.WriteLine("第一次开始"); _mainEvent.Set(); Thread.Sleep(TimeSpan.FromSeconds(2)); _mainEvent.Reset(); Console.WriteLine("第一次关闭"); Thread.Sleep(TimeSpan.FromSeconds(10)); Console.WriteLine("第二次开始"); _mainEvent.Set(); Thread.Sleep(TimeSpan.FromSeconds(2)); Console.WriteLine("第二次关闭"); _mainEvent.Reset(); Console.ReadKey(); } static ManualResetEventSlim _mainEvent = new ManualResetEventSlim(false); static void Method(string threadName, int seconds) { Console.WriteLine("{0}暂停", threadName); Thread.Sleep(TimeSpan.FromSeconds(seconds)); Console.WriteLine("{0}等待打开", threadName); _mainEvent.Wait(); Console.WriteLine("{0}进入", threadName); } 
CountDownEvent
示在计数变为零时处于有信号状态的同步基元.通过CountdownEvent可以在主线程中线程池中的任务运行,主线程要等待线程池中的任务完成之后才能继续。CountdownEvent Class在使用上十分的简单,只要在CountdownEvent的构造函数中传入信号量的数量。在每个线程启动的地方主线程调用AddCount方法增加信号量计数,线程池中跑的线程调用Signal。然后在主线程中调用Signal和Wait方法,就可以实现主 线程等待X次Signal方法调用之后继续。
static void Main() { CountdownEvent cde = new CountdownEvent(3); // 创建SemaphoreSlim 初始化信号量最多计数为3次 Console.WriteLine(" InitialCount={0}, CurrentCount={1}, IsSet={2}", cde.InitialCount, cde.CurrentCount, cde.IsSet); Task t1 = Task.Factory.StartNew(() => { while (true) { Thread.Sleep(1000); if (!cde.IsSet) { cde.Signal(); Console.WriteLine(" InitialCount={0}, CurrentCount={1}, IsSet={2}", cde.InitialCount, cde.CurrentCount, cde.IsSet); } } }); cde.Wait(); /*将 CurrentCount 重置为 InitialCount 的值。*/ Console.WriteLine("将 CurrentCount 重置为 InitialCount 的值。"); cde.Reset(); cde.Wait(); /*将 CurrentCount 重置为 5*/ Console.WriteLine("将 CurrentCount 重置为 5"); cde.Reset(5); cde.AddCount(2); cde.Wait(); /*等待任务完成*/ Task.WaitAll(t1); Console.WriteLine("任务执行完成"); /*释放*/ cde.Dispose(); Console.ReadLine(); } 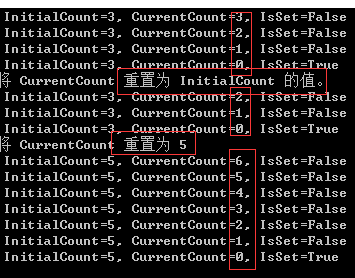
static void Main() { CountdownEvent cde = new CountdownEvent(3); // 创建SemaphoreSlim 初始化信号量最多计数为3次 Console.WriteLine(" InitialCount={0}, CurrentCount={1}, IsSet={2}", cde.InitialCount, cde.CurrentCount, cde.IsSet); /*创建任务执行计数*/ Task t1 = Task.Factory.StartNew(() => { for (int index = 0; index <= 5; index++) { /*重置计数器*/ cde.Reset(); /*创建任务执行计数*/ while (true) { Thread.Sleep(1000); if (!cde.IsSet) { cde.Signal(); Console.WriteLine("第{0}轮计数 CurrentCount={1}", index, cde.CurrentCount); } else { Console.WriteLine("第{0}轮计数完成", index); break; } } /*等待计数完成*/ cde.Wait(); } }); t1.Wait(); /*释放*/ cde.Dispose(); Console.ReadLine(); } 
Barrier
使多个任务能够采用并行方式依据某种算法在多个阶段中协同工作。
当在需要一组任务并行地运行一连串的阶段,但是每一个阶段都要等待其他任务完成前一阶段之后才能开始时,您可以通过使用Barrier类的实例来同步这一类协同工作
private static Task[] _CookTasks { get; set; } private static Barrier _barrier { get; set; } /*获取当前计算机处理器数*/ private static int _particpants = Environment.ProcessorCount; /* * 代码中 展示煮饭的步骤 1.打水 2.淘米 3.放入锅中 4.盖上锅盖 5.生火煮饭 */ static void Main(string[] args) { Console.WriteLine("定义{0}个人煮饭3次", _particpants); _CookTasks = new Task[_particpants]; _barrier = new Barrier(_particpants, (barrier) => { Console.WriteLine("当前阶段:{0}", barrier.CurrentPhaseNumber); }); Stopwatch swTask1 = new Stopwatch(); swTask1.Start(); /*定义N个人*/ for (int cook_person = 0; cook_person < _particpants; cook_person++) { _CookTasks[cook_person] = Task.Factory.StartNew((num) => { int index = Convert.ToInt32(num); /*每个人煮3次饭*/ for (int cook_count = 0; cook_count < 3; cook_count++) { CookStepTask1(index, cook_count); CookStepTask2(index, cook_count); CookStepTask3(index, cook_count); CookStepTask4(index, cook_count); CookStepTask5(index, cook_count); } }, cook_person); } /*ContinueWhenAll 提供一组任务完成后 延续方法*/ var finalTask = Task.Factory.ContinueWhenAll(_CookTasks, (tasks) => { /*等待任务完成*/ Task.WaitAll(_CookTasks); swTask1.Stop(); Console.WriteLine("采用并发 {1}个人煮3次饭耗时:{0}", swTask1.ElapsedMilliseconds, _particpants); /*释放资源*/ _barrier.Dispose(); }); Thread.Sleep(4000); Stopwatch swTask = new Stopwatch(); swTask.Start(); /*定义N个人*/ for (int cook_person = 0; cook_person < _particpants; cook_person++) { /*每个人煮3次饭*/ for (int cook_count = 0; cook_count < 3; cook_count++) { CookStep1(cook_person, cook_count); CookStep2(cook_person, cook_count); CookStep3(cook_person, cook_count); CookStep4(cook_person, cook_count); CookStep5(cook_person, cook_count); } } swTask.Stop(); Console.WriteLine("不采用并发 {1}个人煮3次饭耗时:{0}", swTask.ElapsedMilliseconds, _particpants); Thread.Sleep(2000); Console.ReadLine(); } /*1.打水*/ private static void CookStepTask1(int pesron_index, int index) { Console.WriteLine("{0} 第{1}次 打水... 耗时2分钟", pesron_index, index); Thread.Sleep(200); /*存在线程暂停 所以需要将 _barrier.SignalAndWait();放在方法中 */ _barrier.SignalAndWait(); } /*2.淘米*/ private static void CookStepTask2(int pesron_index, int index) { Console.WriteLine("{0} 第{1}次 淘米... 耗时3分钟", pesron_index, index); Thread.Sleep(300); /*存在线程暂停 所以需要将 _barrier.SignalAndWait();放在方法中 */ _barrier.SignalAndWait(); } /*3.放入锅中*/ private static void CookStepTask3(int pesron_index, int index) { Console.WriteLine("{0} 第{1}次 放入锅中... 耗时1分钟", pesron_index, index); Thread.Sleep(100); /*存在线程暂停 所以需要将 _barrier.SignalAndWait();放在方法中 */ _barrier.SignalAndWait(); } /*4.盖上锅盖*/ private static void CookStepTask4(int pesron_index, int index) { Console.WriteLine("{0} 第{1}次 盖上锅盖... 耗时1分钟", pesron_index, index); Thread.Sleep(100); /*存在线程暂停 所以需要将 _barrier.SignalAndWait();放在方法中 */ _barrier.SignalAndWait(); } /*5.生火煮饭*/ private static void CookStepTask5(int pesron_index, int index) { Console.WriteLine("{0} 第{1}次 生火煮饭... 耗时30分钟", pesron_index, index); Thread.Sleep(500); /*存在线程暂停 所以需要将 _barrier.SignalAndWait();放在方法中 */ _barrier.SignalAndWait(); } /*1.打水*/ private static void CookStep1(int pesron_index, int index) { Console.WriteLine("{0} 第{1}次 打水... 耗时2分钟", pesron_index, index); Thread.Sleep(200); } /*2.淘米*/ private static void CookStep2(int pesron_index, int index) { Console.WriteLine("{0} 第{1}次 淘米... 耗时3分钟", pesron_index, index); Thread.Sleep(300); } /*3.放入锅中*/ private static void CookStep3(int pesron_index, int index) { Console.WriteLine("{0} 第{1}次 放入锅中... 耗时1分钟", pesron_index, index); Thread.Sleep(100); } /*4.盖上锅盖*/ private static void CookStep4(int pesron_index, int index) { Console.WriteLine("{0} 第{1}次 盖上锅盖... 耗时1分钟", pesron_index, index); Thread.Sleep(100); } /*5.生火煮饭*/ private static void CookStep5(int pesron_index, int index) { Console.WriteLine("{0} 第{1}次 生火煮饭... 耗时30分钟", pesron_index, index); Thread.Sleep(500); }
ReaderWriterLockSlim
读写锁的概念很简单,允许多个线程同时获取读锁,但同一时间只允许一个线程获得写锁,因此也称作共享-独占锁。
http://www.cnblogs.com/xchit/p/4548392.html
class Program { static void Main(string[] args) { new Thread(() => Read("读线程1")) { IsBackground = true }.Start(); new Thread(() => Read("读线程2")) { IsBackground = true }.Start(); new Thread(() => Read("读线程3")) { IsBackground = true }.Start(); new Thread(() => Write("写线程1")){ IsBackground = true }.Start(); new Thread(() => Write("写线程2")){ IsBackground = true }.Start(); Thread.Sleep(TimeSpan.FromSeconds(30)); Console.ReadKey(); } static ReaderWriterLockSlim _rw = new ReaderWriterLockSlim(); static Dictionary _items = new Dictionary (); static void Read(string ThreadName) { //Console.WriteLine(ThreadName); while (true) { try { _rw.EnterReadLock(); foreach (var key in _items.Keys) { Thread.Sleep(TimeSpan.FromSeconds(0.1)); Console.WriteLine("{0}读{1}", ThreadName,key.ToString()); } } finally { _rw.ExitReadLock(); } } } static void Write(string threadName) { while (true) { try { int newKey = new Random().Next(250); _rw.EnterUpgradeableReadLock(); if (!_items.ContainsKey(newKey)) { try { _rw.EnterWriteLock(); _items[newKey] = 1; Console.WriteLine("{0}写{1}", threadName,newKey); } finally { _rw.ExitWriteLock(); } } Thread.Sleep(TimeSpan.FromSeconds(0.1)); } finally { _rw.ExitUpgradeableReadLock(); } } } }